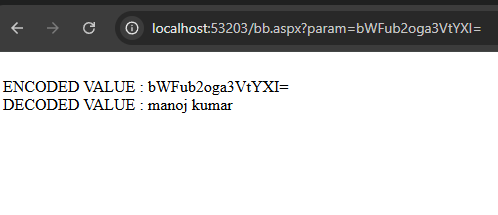
ASPX pages need to pass some parameters in url browser. Ex- destination.aspx?param=abcd . This values when can be misused when directly read by the user. So we should encrypt the same before running the page. In this web application the output page (bb.aspx) will have encoded and decoded value as given below.
OUTPUT:
1a. First Page : aa.aspx [Form]
<div>
<asp:TextBox ID="TextBox1" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" OnClick="Button1_Click" Text="Button" />
<br/>
<asp:Label ID="Label1" runat="server" Text="Label"></asp:Label>
</div>1b. Encoding Before Passing to URL [Code Behind]
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string parameterValue = TextBox1.Text;
string encodedValue = EncodeBase64(parameterValue);
Response.Redirect("bb.aspx?param=" + encodedValue);
}
public string EncodeBase64(string plainText)
{
byte[] plainTextBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(plainText);
return Convert.ToBase64String(plainTextBytes);
}
2a. Second Page : bb.aspx [Form]
<div>
<br/>
<asp:Label ID="Label1" runat="server" Text="Label"></asp:Label>
<br />
<asp:Label ID="Label2" runat="server" Text="Label"></asp:Label>
</div>2b. Decoding After Receiving in Destination Page [Code Behind]
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string encodedValue = Request.QueryString["param"];
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(encodedValue))
{
string decodedValue = DecodeBase64(encodedValue);
Label1.Text = "ENCODED VALUE : " + Request.QueryString["param"];
Label2.Text = "DECODED VALUE : " + decodedValue;
}
}
3. If some reserved characters are required to be passed from URL ,
HttpUtility.UrlEncode(desc) converts reserved characters (like spaces, &, ?, etc.) into their percent-encoded equivalents (e.g., → %20, & → %26).
int rowind = ((GridViewRow)(sender as Control).NamingContainer).RowIndex;
desc = GridView1.Rows[rowind].Cells[4].Text;
string encodedDesc = System.Web.HttpUtility.UrlEncode(desc);
Study Encryption in URL here.